Massage Therapist
Summary
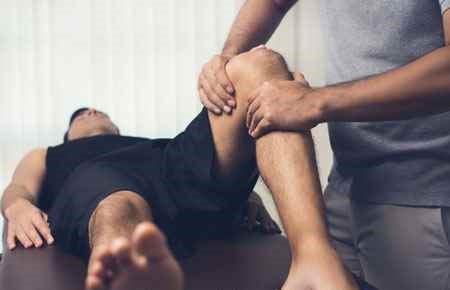
Massage therapists treat clients by using touch to manipulate the muscles and other soft tissues of the body.
What they do
With their touch, therapists relieve pain, help heal injuries, improve circulation, relieve stress, increase relaxation, and aid in the general wellness of clients.
Massage therapists typically do the following:
- Talk with clients about their symptoms, medical history, and desired results
- Evaluate clients to locate painful or tense areas of the body
- Manipulate muscles and other soft tissues of the body
- Provide clients with guidance on stretching, strengthening, overall relaxation, and how to improve their posture
- Document clients’ conditions and progress
Massage therapists use touch to treat clients’ injuries and to promote the clients’ general wellness. They use their hands, fingers, forearms, elbows, and sometimes feet to knead muscles and soft tissues of the body.
Massage therapists may use lotions and oils, and massage tables or chairs, when treating a client. A massage can be as short as 5–10 minutes or could last more than an hour.
Massage therapists talk with clients about what they hope to achieve through massage. They may suggest personalized treatment plans for their clients, including information about additional relaxation techniques to practice between sessions.
Massage therapists can specialize in many different types of massage or modalities. Swedish massage, deep-tissue massage, and sports massage are just a few of the many modalities of massage therapy. Most massage therapists specialize in several modalities, which require different techniques.
The type of massage given typically depends on the client’s needs and physical condition. For example, massage therapists may use a special technique for elderly clients that they would not use for athletes. Some forms of massage are given solely to one type of client; for example, prenatal massage is given only to pregnant women.
Work Environment
Some massage therapists travel to clients’ homes or offices to give a massage. Others work out of their own homes. Many massage therapists, especially those who are self-employed, provide their own table or chair, sheets, pillows, and body lotions or oils.
A massage therapist’s working conditions depend heavily on the venue in which the massage is performed and on what the client wants. For example, when giving a massage to help clients relax, massage therapists generally work in dimly lit settings and use candles, incense, and calm, soothing music. In contrast, a massage meant to help rehabilitate a client with an injury may be conducted in a well-lit setting with several other people receiving treatment in the same room.
How to become a Massage Therapist
Massage therapists typically complete a postsecondary education program of 500 or more hours of study and experience, although standards and requirements vary greatly by state or other jurisdiction. Most states regulate massage therapy and require massage therapists to have a license or certification.
Education requirements for massage therapists vary greatly by state or locality. Education programs are typically found in private or public postsecondary institutions. Most programs require at least 500 hours of study for their completion; some programs require 1,000 or more hours.
A high school diploma or equivalent is usually required for admission to a massage therapy program. Programs generally include both classroom study and hands-on practice of massage techniques. Programs cover subjects such as anatomy; physiology, which is the study of organs and tissues; kinesiology, which is the study of motion and body mechanics; pathology, which is the study of disease; business management; and ethics.
Programs may concentrate on certain modalities, or specialties, of massage. Several programs also offer job placement services and continuing education. Both full-time and part-time programs are available.
In 2016, 45 states and the District of Columbia regulated massage therapy. Although not all states license massage therapy, they may have regulations at the local level.
In states with massage therapy regulations, workers must get a license or certification before practicing massage therapy. State regulations typically require graduation from an approved massage therapy program and passing an exam.
The exam may be a state-specific exam or the Massage and Bodywork Licensing Examination (MBLEx) licensure exam, offered by the Federation of State Massage Therapy Boards.
Massage therapists also may need to pass a background check, have liability insurance, and be certified in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Many states require massage therapists to complete continuing education credits and to renew their license periodically. Those wishing to practice massage therapy should look into legal requirements for the state and locality in which they intend to practice.
Pay
The median annual wage for massage therapists was $42,820 in May 2019. The median wage is the wage at which half the workers in an occupation earned more than that amount and half earned less. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $21,810, and the highest 10 percent earned more than $80,630.
Job Outlook
Employment of massage therapists is projected to grow 21 percent from 2019 to 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations. Continued growth in the demand for massage services will lead to new openings for massage therapists.
As more states adopt licensing requirements and standards for massage therapists, the practice of massage is likely to be respected and accepted by more people as a way to treat pain and to improve overall wellness.
Similarly, demand will likely increase as more healthcare providers understand the benefits of massage and these services become part of treatment plans. However, demand in some healthcare settings will be tempered by limited insurance coverage for massage services.
Massage also offers specific benefits to particular groups of people whose continued demand for massage services will lead to overall growth for the occupation. For example, many sports teams hire massage therapists to help their athletes rehabilitate from injuries and to relieve or manage pain.
The number of massage clinic franchises has increased in recent years. Many franchised clinics offer more affordable massages than those provided at spas and resorts, making massage services available to a wider range of customers.
Similar Job Titles
Bodywork Therapist, Certified Massage Therapist (CMT), Clinical Massage Therapist, Integrated Deep Tissue Massage Therapist, Licensed Massage Practitioner (LMP), Licensed Massage Therapist, Massage Therapist, Medical Massage Therapist, Registered Massage Therapist, Therapeutic Massage Technician
Related Occupations
Self-Enrichment Education Teacher, Barber, Skincare Specialist, Fitness Trainer and Aerobics Instructor, File Clerk
More Information
The trade associations listed below represent organizations made up of people (members) who work and promote advancement in the field. Members are very interested in telling others about their work and about careers in those areas. As well, trade associations provide opportunities for organizational networking and learning more about the field’s trends and directions.
- American Massage Therapy Association
- Associated Bodywork and Massage Professionals
- International Association of Healthcare Practitioners
- National Certification Board for Therapeutic Massage and Bodywork
- Zero Balancing Health Association
Magazines and Publications
Whether a patient calls for a relaxing treat… or help recovering from an injury…. massage therapists provide an important part of their wellness care. While massage is popular now due to the natural health movement and interest in prevention, massage therapy has its roots in ancient health care practices. Massage therapists massage and knead patients’ soft tissues to treat medical conditions, injuries, or to maintain health. Using their knowledge of basic anatomy, they may assess range of motion and tissue condition to determine the best techniques to use. Talking with patients beforehand about their symptoms is as important as maintaining communication throughout the massage and keeping health records afterward. Massage therapists learn particular techniques, like sports massage, reflexology, or deep tissue massage. They may work for themselves, in a rehabilitation practice, a massage clinic, at a spa, or even for a sports team. Massage therapists must typically complete a training program, typically between 500-1000 hours of study, to develop these specialized skills. Most states also have licensure and practice requirements. Becoming a massage therapist can be a first step in a health care career. Many health care providers understand the benefits of massage, and include these services in their treatment plans. Whichever setting these professionals choose, their skills are a welcome addition to their patients’ care.
Content retrieved from: US Bureau of Labor Statistics-OOH www.bls.gov/ooh,
CareerOneStop www.careeronestop.org, O*Net Online www.onetonline.org
